While the world has returned to normal life from the COVID-19 pandemic, the virus continues to evolve.
On August 9, the World Health Organization upgraded the new coronavirus variant EG.5 to a strain that “needs attention”. This move shows that this authoritative health agency believes that EG.5 should be further tracked and studied.
EG.5 is from the Omicron family and is a subvariant of XBB.1.9.2. However, EG.5 is also constantly evolving, and currently has its own branch EG.5.1.
The US media stated that the EG.5 mutant strain of the new coronavirus is rapidly spreading in the United States, and the number of new coronavirus infection cases has surged. The French health department has also noticed that the number of hospitalizations related to the new crown infection has increased recently, and the variant of the EG.5 strain accounts for the majority of new cases in France.
EG.5 triggered a surge in the number of hospitalizations in the United States
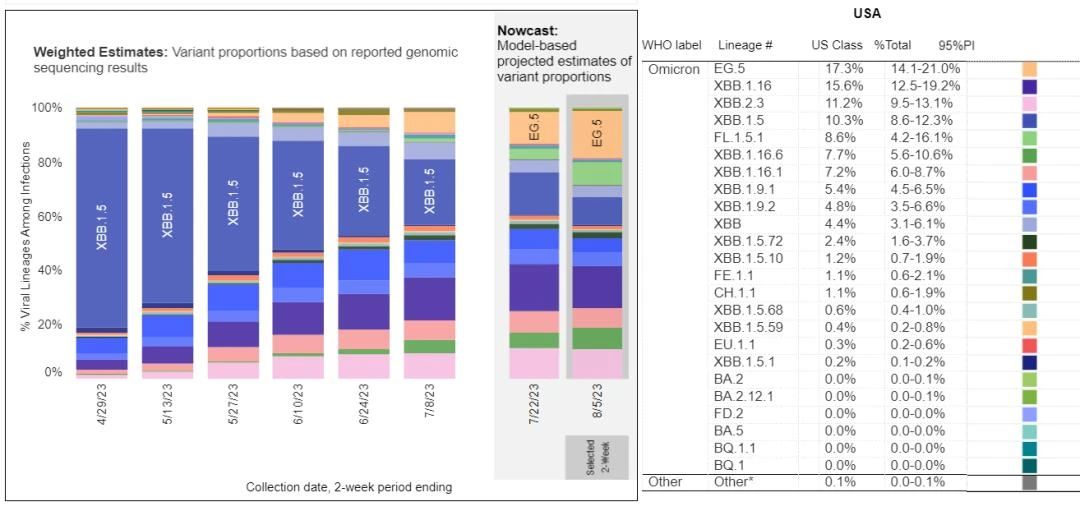
According to the latest estimates from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the EG. Nationally, EG.5 accounts for about 17 percent of new cases in the country, while the other most common strain, XBB.1.16, accounts for 16 percent of cases.
According to the New York Post report, the latest data released by the New York State Department of Health on August 2 showed that since the previous week, the number of new coronavirus infection cases has surged by 55%, with an average of 824 cases reported per day across the state. Hospitalizations for the disease have risen by 22% compared to the previous week, meaning more than 100 people are hospitalized every day.
The rise in cases of the novel coronavirus is not limited to New York. Hospitalizations for COVID-19 have been increasing across the United States, with the number of hospitalizations rising 12.5% in the latest week to 9,056, according to the federal health agency.
Due to the shortage of new coronavirus detection kits, local medical care will face considerable pressure. In June, the Biden administration stopped mailing free test kits, and kits that people had stockpiled for the past year or two were about to expire. Anna Burstyn, an assistant professor in the Department of Population Health at New York University School of Medicine, told The Post, “Without testing, it is very difficult for people to know if they have a new coronavirus infection, and the lack of available test kits may increase the number of new coronavirus infections. Number of hospitalizations and deaths from coronavirus infection.”
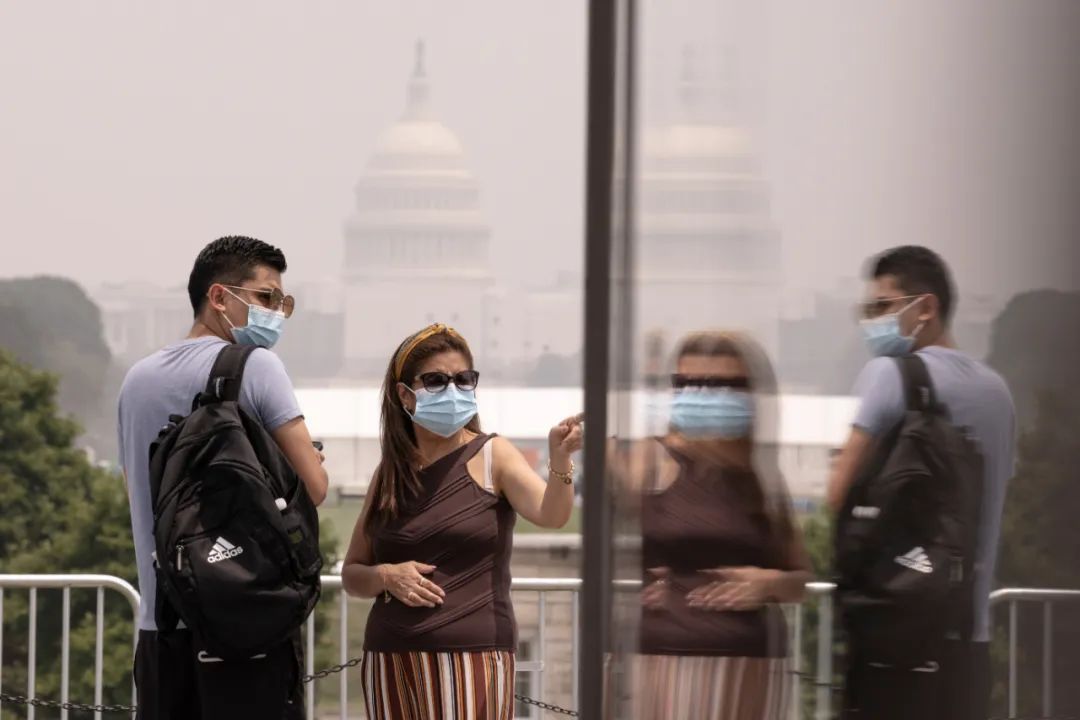
On June 29, in Washington, the capital of the United States, tourists wearing masks visited the Washington Monument, and the Capitol in the distance was shrouded in smoke. Photo source: Photo by Aaron from Xinhua News Agency
The UK is also receiving the addition of the EG.5 variant. The British health agency estimated on July 20 that nearly 15% of new cases in the UK were caused by new variants, increasing at a rate of 20% every week.
On August 9, local time, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that the new coronavirus variant EG.5 was listed as a variant that “needs attention”, but based on currently available evidence, WHO still believes that EG. The public health risk is Low.
The World Health Organization divides the variants of the new coronavirus into three levels, from low to high, which are “monitored”, “requires attention” and “requires attention”. On July 19, WHO listed EG.5 as a “monitored” level for the first time.
Globally, EG.5 accounted for 11.6% of weekly cases in mid-July, up from 6.2% four weeks earlier, according to the WHO.
Maria van Kerkhove, the WHO technical lead for the new crown epidemic, also said that although the infectivity of EG. No changes in the severity of EG.5 were detected compared to other sublines of Rong.
Epidemiologists pointed out that record high temperatures have prompted more people to use air conditioners indoors, which has helped spread the virus. Unless there is evidence that EG.5 or a substrain of it is causing more severe disease, public health officials’ advice and guidance remains the same, including asking people to assess risk tolerance, remain vigilant and keep up to date with the latest vaccines, experts said Vaccination status.
New variants dominate in France
According to overseas news, the French health department has noticed that the number of hospitalizations related to the new crown infection has recently increased, and a variant called Eris (EG.5 strain) accounts for the majority of new cases in France. It should be noted that although some websites and social media netizens have named this mutant strain “Eris” according to the Greek alphabet, this has not been officially announced by the WHO.
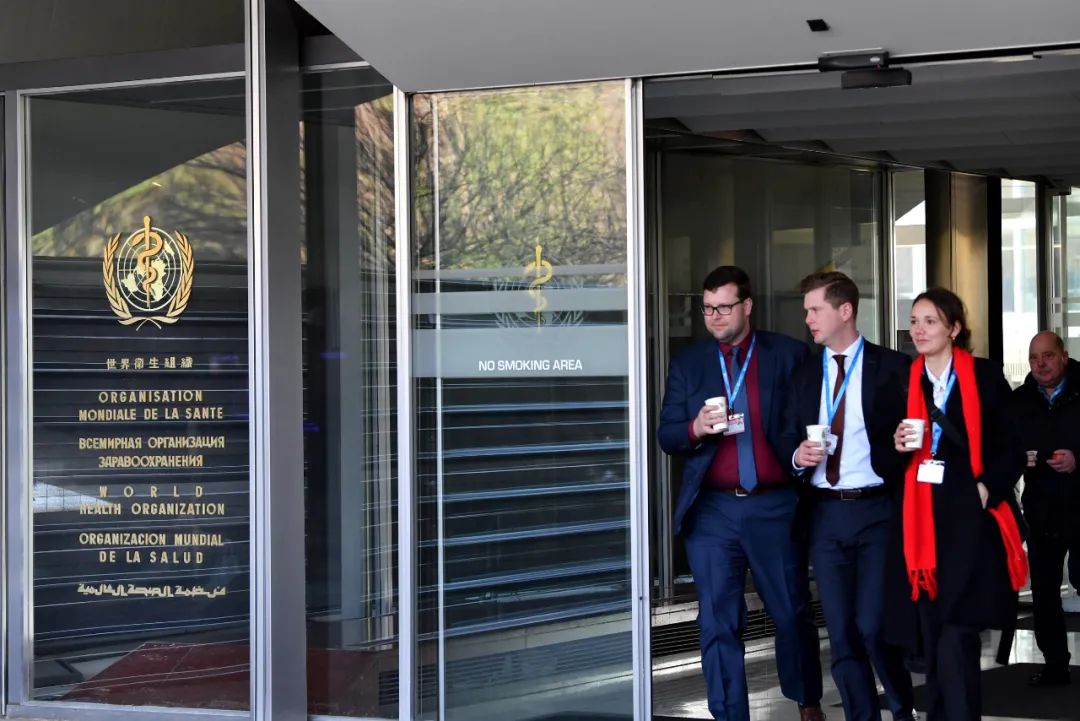
On January 30, in Geneva, Switzerland, staff members walked out of the headquarters building of the World Health Organization. Photo source: Photo by Xinhua News Agency reporter Lian Yi
According to a French TV report on the 7th, the French Public Health Agency introduced that the number of new coronavirus infections is increasing in all age groups in France, especially among adults. There have also been clusters of new crown infections in France recently, especially during the “Bayonne Festival”, when the sales of new crown testing reagents in pharmacies in the southwestern region surged.
A new variant of the new coronavirus, Eris, may be responsible for this phenomenon. People infected with Eris now account for about 35 percent of new cases in France, a higher proportion than other variants, according to the Pasteur Institute in France.
Eris appears to be more transmissible than the XBB variant it is rapidly replacing, but there is no evidence that it poses a higher risk of serious infection, Antoine Fraoux, director of the Geneva Institute for Global Health in Switzerland, explained in an interview with France 1 TV. , and there is no evidence that it is better able to escape the immune protection obtained by previous infection or vaccination with the new crown vaccine. The main groups currently at risk of severe infection with the new crown are still immunocompromised persons and the elderly.
Antoine Fraoux warned that the fall of 2023 could usher in a new wave of the epidemic, but it would not necessarily be worse than the one of the past year.
Prevention of virus transmission
Understanding Airborne Transmission: Explain the concept of airborne transmission of viruses and bacteria, emphasizing how respiratory droplets and aerosols can carry infectious particles through the air.
Air Purification Technology including:
- HEPA Filters: Describe the role of High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters in air purifiers. These filters can capture particles as small as 0.3 microns, which includes many viruses and bacteria.
- UV-C Technology: Discuss the use of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UV-C) in air purifiers. UV-C light can deactivate microorganisms by disrupting their DNA, preventing them from replicating.
- Ionic and Electrostatic Filters: Explain how these technologies attract and trap particles using charged plates, which can include viruses and bacteria.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Highlight the role of activated carbon filters in adsorbing odors, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and potentially some viruses and bacteria.
- Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO): Mention PCO technology, which uses UV-C light to activate a catalyst and create reactive molecules that break down pollutants, including biological particles.
Emphasize that while air purifiers can help reduce airborne particles, they are not a standalone solution and should be used in conjunction with other preventive measures.
Encourage users to choose air purifiers with HEPA filters and other relevant technologies for virus and bacteria removal.
Welcome to come to us to consult professional air governance related problems, we have many years of rich and professional air governance solutions and patented technology, for classrooms, schools, hospitals, homes, bedrooms and other scenarios.
Post time: Aug-07-2023